A Multifaceted action of Phytochrome B in Plant Environmental edition
Creation
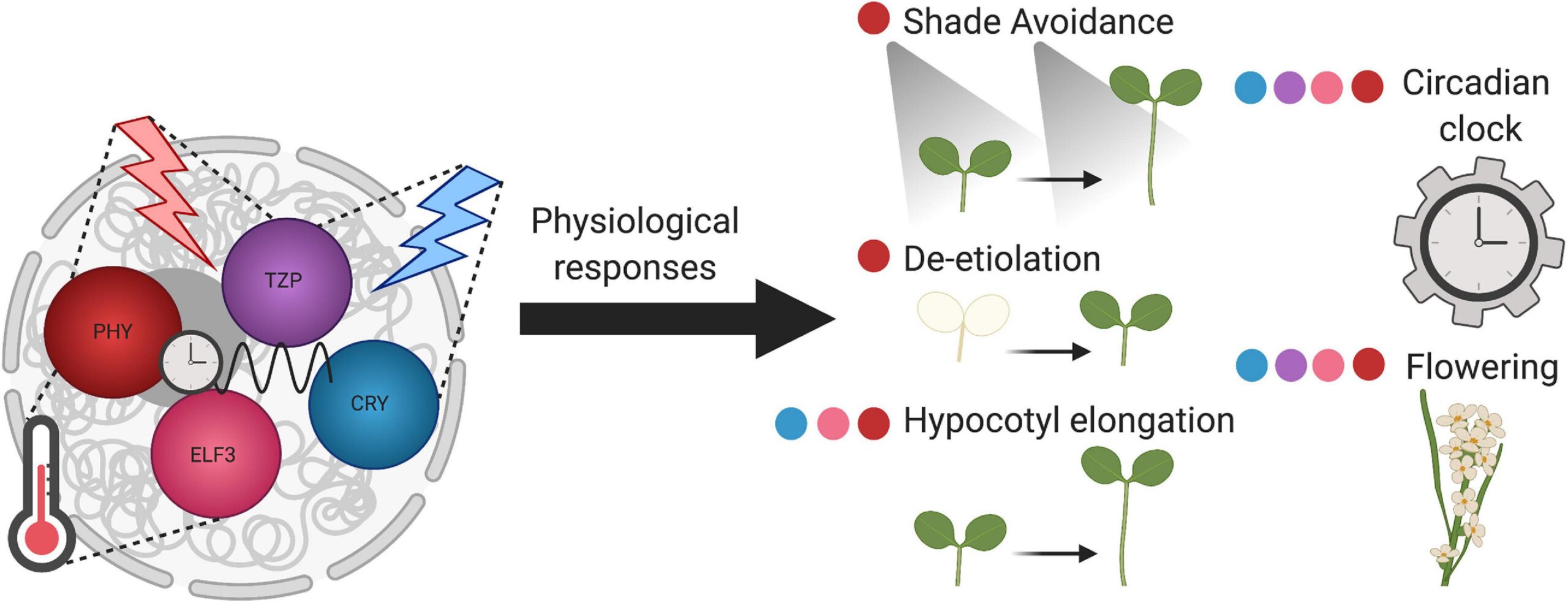
Flowers are sessile organisms that have developed various mechanisms to conform to their ever-converting surroundings. One crucial thing in plant adaptation is light, which serves as a supply of strength for photosynthesis and as a sign for diverse developmental procedures. Phytochromes are a category of photoreceptors that play an important position in perceiving and responding to light alerts in flora.
Among the five phytochromes recognized in Arabidopsis thaliana, phytochrome B (phyB) is the most considerably studied. it’s been shown to have a multifaceted action in plant environmental adaptation, affecting numerous aspects of plant growth and development. This text aims to discover the numerous features of phyB in plant adaptation to environmental cues.
PhyB structure and Photoconversion
Phyb is a crimson/a ways-purple light photoreceptor that undergoes reversible photoconversion among two forms: the biologically energetic Pr (red light-soaking up) form and the inactive Pfr (far-purple light-absorbing) form.
This photoconversion is critical for phyB’s function as a mild sensor. inside the dark, phyB predominantly exists inside the Pr form, and exposure to red light converts it to the Pfr shape, which initiates a signaling cascade mainly to diverse physiological responses. subsequent exposure to far-pink light converts Pfr returned to Pr, terminating the signaling cascade.
PhyB and Seed Germination
Seed germination is a critical stage in a plant’s lifestyle cycle, and mild plays an essential position in regulating this technique. PhyB has been proven to be a key regulator of seed germination, with its movement depending on the mild conditions. In crimson light, phyB promotes seed germination by inhibiting the hobby of the transcription thing PIF1, which represses germination-selling genes.
In evaluation, beneath a ways-crimson mild, phyB promotes seed dormancy via stabilizing PIF1 and preventing germination-promoting gene expression. This dual position of phyB in seed germination lets plants reply to one-of-a-kind mild conditions and optimize their germination timing for foremost increase and survival.
PhyB and shade Avoidance
Flowers growing in dense flora regularly experience decreased purple to a long way-red (R:FR) ratio, indicating the presence of neighboring vegetation. This low R:FR ratio triggers a set of responses collectively called shade avoidance syndrome (SAS), allowing flora to compete for light assets. PhyB is an essential participant in SAS, because it perceives the modifications in R:FR ratio and initiates adaptive responses.
Under the low R:FR ratio, phyB is rapidly transformed to the Pfr shape, mainly due to the degradation of the transcription component PIF4. PIF4 degradation relieves its inhibitory impact on elongation boom, selling stem elongation and leaf hyponasty, which enables plants outgrow their buddies and advantage to get right of entry to more mild. Moreover, phyB additionally regulates the expression of genes involved in branching, leaf senescence, and flowering time, in addition contributing to color avoidance responses.
PhyB and Photomorphogenesis
Photomorphogenesis refers to the light-brought developmental tactics that arise in flora, along with seedling de-etiolation and chloroplast improvement. PhyB plays an important function in these techniques by regulating the expression of genes worried in light perception and signaling. inside the darkish, phyB represses the activity of transcription factors called PIFs, which promote etiolated increase.
Upon exposure to mild, phyB is converted to the Pfr shape, leading to the degradation of PIFs and the activation of genes concerned in chlorophyll biosynthesis, chloroplast development, and photomorphogenesis. This lets in seedlings to undergo greening and set up photosynthetic capability, enabling them to utilize light strength for boom and survival.
PhyB and Flowering Time
Flowering time is a crucial trait that determines a plant’s reproductive fulfillment. PhyB has been proven to play a function in regulating flowering time by way of integrating mild and temperature signals. underneath lengthy-day situations, phyB promotes flowering by activating the expression of the key flowering time regulator CONSTANS (CO). CO, in flip, turns on the expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (feet), a mobile signaling molecule that promotes flowering.
In assessment, beneath quick-day situations, phyB inhibits flowering by repressing CO expression. In addition, phyB also interacts with different flowering time regulators, such as GIGANTEA (GI) and PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING component three (PIF3), further fine-tuning the flowering time reaction to converting environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Phytochrome B is a flexible photoreceptor that plays a multifaceted function in plant environmental versions. Its capacity to perceive and reply to mild indicators permits plants to optimize their boom and development below distinct environmental situations.
From seed germination to flowering time law, phyB’s action is intricately connected to numerous aspects of plant physiology. know-how the molecular mechanisms underlying phyB’s features will now not handiest offer insights into fundamental plant biology however also pave the manner for developing techniques to enhance crop yield and resilience inside the face of converting environmental conditions
Read more about cytokinesis