What are the Different Types of ELISA Assays?
If you’re delving into the fascinating world of immunology and biochemistry, you’ve likely encountered the term ELISA. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, or ELISA for short, is a versatile and powerful technique used to detect and quantify specific substances, such as proteins, peptides, antibodies, and hormones, in various biological samples. In this article, we’ll take a comprehensive look at the different types of ELISA assays, how they work, and their applications in research and diagnostics.
1. Introduction to ELISA Assays
Elisa Washers are widely used in research, clinical laboratories, and pharmaceutical industries due to their sensitivity and specificity in detecting analytes of interest. They rely on the principle of antigen-antibody interaction, where a target molecule (antigen) is captured by an immobilized antibody or vice versa.
2. Competitive ELISA
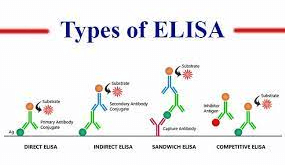
Competitive ELISA involves competition between the labeled antigen and the unlabeled antigen from the sample for binding sites on the immobilized antibody. The signal is inversely proportional to the concentration of the analyte.
3. Indirect ELISA
Indirect ELISA detects antibodies present in a sample. The immobilized antigen binds the antibodies, and a secondary enzyme-labeled antibody is used for detection. This type is highly sensitive and allows for signal amplification.
4. Sandwich ELISA
Sandwich ELISA is used to detect and quantify antigens. It involves immobilizing a capture antibody, binding the target antigen, and then detecting it with a labeled detection antibody. This approach offers high specificity and is often used in disease diagnostics.
5. Direct ELISA
Direct ELISA directly detects antigens using an immobilized antibody. It’s a simple and rapid technique but may have limitations in sensitivity compared to other methods.
6. Reverse ELISA
Reverse ELISA detects antibodies by using immobilized antigens. This method is useful for studying autoimmune diseases and determining the presence of specific antibodies in patient samples.
7. Multiplex ELISA
Multiplex ELISA allows the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in a single sample. It’s efficient and reduces sample consumption, making it valuable in biomarker discovery and high-throughput screening.
8. Quantitative vs. Qualitative ELISA
ELISA assays can provide both quantitative and qualitative results, depending on the experimental setup and the type of assay used. Quantitative ELISA measures the concentration of an analyte, while qualitative ELISA determines the presence or absence of a specific molecule.
9. Steps in Performing an ELISA Assay
Performing an ELISA assay involves several key steps, including sample preparation, coating the plate, blocking, antigen or antibody binding, detection, and data analysis.
10. Advantages and Limitations of ELISA Assays
ELISA assays offer high sensitivity, versatility, and a wide dynamic range. However, they may have limitations in terms of cost, time, and the need for specialized equipment.
11. ELISA Assays in Disease Detection
ELISA plays a crucial role in disease detection, from diagnosing infections to monitoring autoimmune disorders and detecting cancer biomarkers.
12. ELISA in Drug Development
In pharmaceutical research, ELISA assays are utilized to screen potential drug candidates, study protein-protein interactions, and assess drug effects on cellular pathways.
13. Future Trends in ELISA Technology
The future of ELISA technology holds promise for further automation, miniaturization, and integration with other analytical techniques, enhancing efficiency and reducing assay times.
Conclusion
In the realm of life sciences, Elisa Washersstand as a cornerstone in the study of biomolecules. Their diverse applications, precision, and ability to provide valuable insights have revolutionized research, diagnostics, and drug development.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What does ELISA stand for? ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.
- What is the principle behind ELISA assays? ELISA assays are based on the principle of antigen-antibody interactions.
- What is the significance of multiplex ELISA? Multiplex ELISA allows simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in a single sample, saving time and resources.
- Can ELISA be used to diagnose diseases? Yes, ELISA is widely used in disease diagnosis, including infectious diseases and cancer.
- What does the future hold for ELISA technology? The future of ELISA includes advancements in automation, miniaturization, and integration with other technologies.
In conclusion, the diverse types of ELISA assays play a pivotal role in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and drug development. From competitive to sandwich assays, each variation contributes uniquely to our understanding of biological molecules and their functions. As technology advances, ELISA’s potential is set to expand further, promising even greater insights into the complex world of molecular interactions and disease mechanisms. So, whether you’re a researcher unraveling the mysteries of the immune system or a clinician diagnosing illnesses, ELISA assays are your reliable allies on this scientific journey.